|
Hotspot versus Dark
Spot
|
|
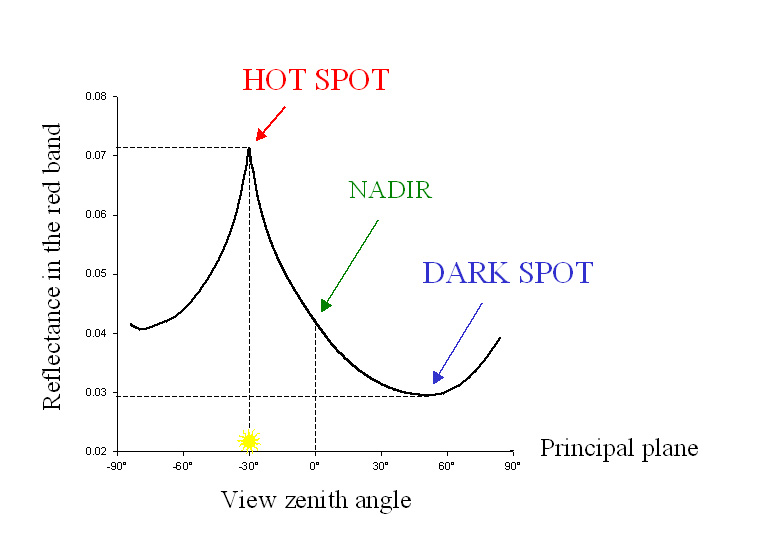
| The hotspot
is a well known feature of the BRDF. The darkspot is the point where the
lowest reflectance is found, usually on the principal plane. |
Chen
et al, 1999 and Lacaze
et al (to be submitted) demonstrated, using Spaceborne POLDER data,
that the index Hot Dark Spot (HDS):
|
HDS =
|
r(hotspot)-r(darkspot)
|
|
|
r(darkspot)
|
|
is related to the clumping index of vegetation. |
To study this effect in more details,
a special mode, built in the USER-DEFINED mode of 5-Scale, has been incorporated
in the interface. Results from this
new mode have been shown by Leblanc
et al, 2001, and a normalize index, NDHD seems more linear than the
HDS:
|
NDHD =
|
r(hotspot)-r(darkspot) |
|
|
r(hotspot)+r(darkspot) |
|
|
| For this mode, several simulations are
needed to find the lowest reflectivity (darkspot). The present version
uses the NIR band to do the calculation. The model computes the reflectance
at view zenith angle on the forward scattering side starting at 25°
and increasing by step of 1° until 80°. |
The clumping is calculated at the solar
zenith angle.
|


